What are the parts of the circulatory system?
The heart is a muscular organ that has two halves. Each half is divided into two chambers: an atrium and a ventricle.
A valve between the two chambers opens and closes to allow the blood to flow in one direction only. Blood does not flow between the two halves of the heart.
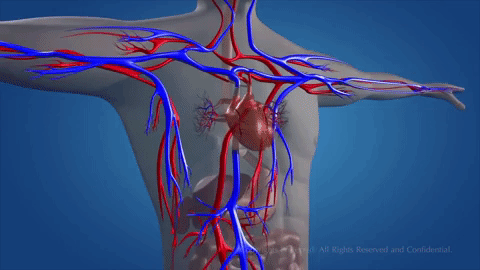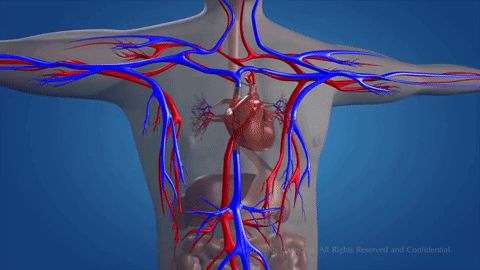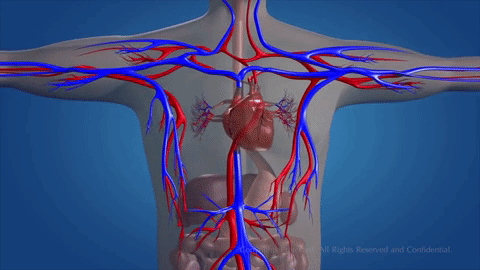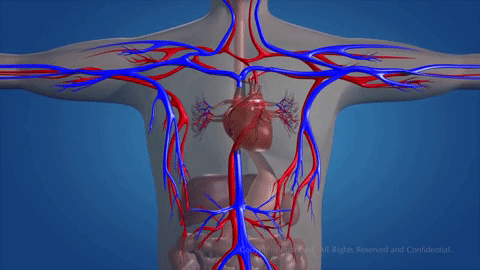
A network of blood vessels transports the blood around the body. The network is made up of three different types of vessels.
• Arteries carry blood away from the heart and around the body.
• Veins carry blood towards the heart.
• Very fine blood capillaries connect the veins and the arteries.
Nutrients, water, oxygen, carbon dioxide and waste substances move from different cells into and out of the capillaries.
What is blood made up of?
Blood is made up of:
• plasma, which is a liquid that contains nutrients, water and waste products.
• red blood cells, which give blood its colour. They contain a red substance called haemoglobin, which transports oxygen and carbon dioxide.
• white blood cells, which form part of the immune system. They help protect the body from infections.
• platelets, which stick together to stop bleeding.
How does the heart beat?
Blood is pushed around the body in a continuous movement called a heartbeat. There are two parts to a heartbeat.
• Diastole. The cavities in the heart expand and blood enters the two atriums. The valve between the atriums and the ventricles opens and blood passes into the ventricles.
• Systole. The cavities in the heart contract and blood leaves the two ventricles and enters the arteries. The right ventricle pumps oxygen-rich blood into the aorta. The left ventricle pumps blood containing carbon dioxide to the pulmonary artery.
How does blood circulate?
Blood flows in a continuous movement around two circuits.
The pulmonary circuit
Blood from the venae cavae enters the right atrium. This blood contains carbon dioxide as well as nutrients and waste substances. It enters the right ventricle and is pumped into the pulmonary artery. Blood travels to the alveoli in the lungs.
Oxygen moves into the blood at the same time. The blood travels along the pulmonary vein until it reaches the left atrium.
The systemic circuit
From the left atrium, blood carrying oxygen flows into the left ventricle and is pumped into the aorta. This artery branches into smaller arteries and arterioles that spread all over the body.
Capillaries at the end of the arteries connect to cells. Oxygen and nutrients in the blood are transferred to the cells. Waste substances pass from the cells into the capillaries. The blood capillaries connect and form veins. Veins join and connect with the venae cavae. Blood travels along the venae cavae into the right atrium, ready to begin the journey again.
























No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario
Nota: solo los miembros de este blog pueden publicar comentarios.